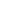
Comfort and safety, the two most important requirements in home textiles were first successfully combined in 1980: with flame retardant FR polyester fibres and yarns.
Textiles made from these fibres and yarns are permanently flame retardant. Unlike fabrics that receive a surface treatment at a later stage, FR polyester textiles offer long-term security.

pacerun:'yes';font-family:Calibri;font-size:12.0000pt;mso-font-kerning:1.0000pt;" >- In event tents
It is stipulated in current requirements of German technical regulations that decoration materials used by exhibitors, event organizers, stand construction companies and service companies have to be flame retardant in compliance with DIN 4102 or DIN EN 13501-1. These technical regulations are usually part of the contract, and the contract parties are liable for compliance. Decoration materials include wall coverings, room partitions, curtains, displays, textile awnings, banners, flags and the like.
This small but decisive difference results from the chemical structure of the polyester fibre. In the shape of a comonomer – a phosphor-organic compound, where the flame retardant properties are firmly anchored in the fibre. It is not possible for external influences to affect them.

Fibres given an additional flame protection finish (right) can lose the protection as a result of wear, age or frequent washing. Flame retardant polyester fibres (left) are inherently flame retardant. For this reason materials made from these fibres and filament yarns are likewise permanently flame retardant.This is an important argument from the ecological aspect as well. Apart from their environmentally friendly manufacture materials in FR polyester require no additional fire protection treatment, such as normally combustible materials need. Treatments of this kind are harmful to the environment. Flame retardant polyester fibres and filaments are, furthermore, certified to Oekotex 100 Standard. In comparative terms only very slight amounts of toxic fumes develop in the event of a fire. This is particularly important, since in a fire the danger of suffocation from smoke fumes is greater than the risk of injury from flames.
























 Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected] Tel: +86-512-63221899
Tel: +86-512-63221899


 English
English Español
Español